 LOCATION AND DEMOGRAPHY LOCATION AND DEMOGRAPHY |
The four natural regions which form guinea
The Republic of guinea covers 245 860 sq km to the west of West Africa 10 north of the equator. It is bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean, on the north by Guinea Bissau, Senegal and Mali, on the East by the Ivory Coast, and on the south by Sierra Leone and Liberia. A former French colony, Guinea was the first francophone African country to gain its independence on 2nd October 1958, after having voted NO in the referendum of 28th September 1958.
Veritable water reserve of West Africa, Guinea gives birth to the large rivers of West Africa (Niger, Senegal, Gambia). It has also Mount Nimba (1752m), the highest West African mountain. Guinea is divided into four natural regions with distinct human, geographic and climatic characteristics.
 Maritime Guinea Maritime Guinea |
It covers 18% of the country. The major ethnic groups are the Soussous, the Bagas, the Nalou, the Landoumas and the Miki Fore. They are excellent rice growers and fishermen. Maritimes Guinea is a flat and narrow coastal plain bordered by estuaries. The major rivers (Rio nunez, Rio Pongo, Konkoure) flow into the sea. The vegetation consists of coconut palms, palm groves and mangroves in the swamp areas. Maritime guinea's climate (South-guinean type) is marked by heavy rains, especially on the side where the monsoon blows.
 Mid-Guinea Mid-Guinea |
It covers 1/5 of the country. Its population is essentially composed of shepherds. It also has the Djallonke and the Coniagui who are farmers. Mid-guinea is dominated by the Fouta-Djallon mountain range whose highest peak, Mount Laura (1515m) is found in the north, in the Mali mountains. The center has high plateau ranging between 600m and 1500m. the most important rivers in the region are the Tinkisso, the Bafing and the Boyoke. The climate, of the Sudanese type, is characterized by low temperatures from November to March that can drop to 16. Rain is abundant in winter.
 Upper guinea Upper guinea |
This savannah region covers 41% of the country. Its population is in the majority of Malinke ethnic origin whose traditional activities are farming, hunting and cattle raising. Upper Guinea is a savannah region suffering in several places, desertification. It is faced with brush fires and deforestation due tot he cut and bum farming system. The Sudanese climate, characteristic of Upper Guinea, is warm and dry with a predominant harmattan in March. The year is divided into two seasons of equal length, the dry season from November to April and winter from May to October.
 Forested Guinea Forested Guinea |
The region is both forested and mountainous. Dense forest is now threatened by intense exploitation of its resources. Forest Guinea is inhabited by an ethnic mosaic: the Kissi live in the Kissidougou and Gneckedou Prefectures; the Kono, the Manon (N'zerekore and Zomou Prefectures), the Thomas, the Thomas Minant (Macenta), the Konianke (Beyla Prefecture). The foresters are cultivators and planters. The economy of Forested Guinea suffers from the distance between the region and the capital, Conakry, where the port and the principal Guinean economic structures are situated.
 WORLD RANKING WORLD RANKING |
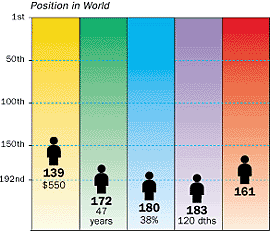

Guinea's estimated population of approximately seven million is composed of a variety of ethnic groups. The present-day boundaries of Guinea were determined by colonial powers with little regard to ethnic and linguistic groups. These boundaries, therefore, often split these groups. Within the country, though, the four major geographic regions largely correspond to the four major ethno-linguistic groups. | Since 1984, and the death of the highly controversial President Sekou Touré, traditional rivalries have reemerged. The largest ethnic group, the Malinke, lost the power they held under Touré, and have suffered reprisals. Today, the coastal peoples, including the Soussou, are dominant, benefiting from renewed rivalry between the two major groups - Malinke and Fulani, the latter based in the highland region of Fouta Jalon.
Daily life in Guinea revolves around the extended family, which survived the climate of suspicion generated by paid informers under Sekou Touré. Women acquired influence within his Marxist party, but a Muslim revival since 1984 has reversed this trend.
 There are 8 main ethnic groups in Guinea. The last census based on ethnicity was in 1955. There are 8 main ethnic groups in Guinea. The last census based on ethnicity was in 1955. |
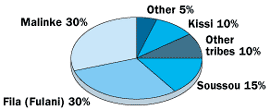
ETHNIC MAKEUP
The Fulbes (singular Pullo) also known as Fulanis (in English), Peuls or Peuhls (in French), Fulfuldes, Futankes etc...The Fulbes are part of a large ethnic group of the Fulanis that are scattered through 18 countries in Africa. Their origin is still a mystery. The language they speak is called Pular (also known as Halpular). The Fulbes are mostly from the central region of Foutah Jalon although now like all other ethnics groups they are everywhere. In the 1955 census the Fulbes were 30% of the Guinean population.
The Maninkas also known as Malinkes (in French) or Mandingo (in English) are mostly from the Upper Guinea region which was part of the various Mandingos empires that ruled there for centuries. The Maninkas are part of the vast group of Mandingo people that live in various parts of West Africa. Their language is the Maninkakan which is spoken in various forms through the region like the Dioula language in Cote d'Ivoire and the Bambara language in Mali. The 1955 census counted 30% of the Guinean population as Maninkas.
The Sosso live in the coastal region of Guinea (including the capital Conakry). The term refers mostly to the language that resulted from melting pot of locals inhabitants and English, French and Portuguese languages. The Sossos in the 1955 census were 15% of the Guinean population.
The Kissiens live in the bordering region of the forest of Guinea.
The Tomas
The Guerzes
The Landoumas
The Mikifores
The Bagas
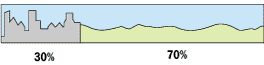
Guinea has a population of 7.164.823 million as of the December 31, 1996 census. Also there are approximately over 2 millions Guineans outside its borders. Mostly in the neighboring countries, Western Europe and North America. 51 % are women and 29.6% live in urban areas. There are 650,000 refugees inside Guinea's borders.
The urban / rural population split
The birth and death rate in Guinea is 50.6 and 20.3 respectively per 1,000 in 1990-95. The life expectancy is 44.5 for males and 45.0 for females. (Source: UN, World Population Prospects. 1999).
|

