 Country
Fact File Country
Fact File |

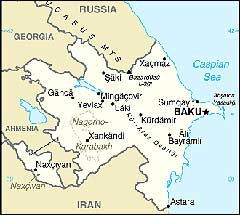
Land Area: 86,600 sq km
Population: 7,830,764 (July 2003
est.)
Population Growth Rate: 0.44% (2003 est.)
Capital: Bak
 Nature
and climate Nature
and climate |
The modern appearance of the territory of
Azerbaijan with its high mountains, volcanic
plateaus, deep mountain canyons and river
valleys, plains and coasts, complex of various
minerals was formed over several hundred millions
of years of geologic history. Diverse and
many-tiered, quaintly divided landscape of
modern Azerbaijan has been formed.
Azerbaijan is called mountain country.
Geo -morphological units are formed by the
peaks of the Greater and Lesser Caucasus,
and the Talish Mountains, which surround
the Kur-Araz lowland. The average height
of the territory of the Republic is 657
meters, however, while Caspian lowland is
below the ocean level by 26 meters, the
highest mountain of the Republic is Bazarduzu
that reaches 4466 meters. The alpine mountain
chains of the Greater Caucasus descend in
the southeastern direction of the peninsula
and go to the Caspian seabed as the underwater
chain. This area has the largest amount
of the mud volcanoes in the world - over
250.
The mountains of the Lesser Caucasus are
less high and consist of numerous mountain
chains and the volcanic Garabag plateau
with the cones of the extinct volcanoes.
The highest mountain is Gapijik (3906 m).
The narrow Samur-Devechi lowland enclosing
the Absheron peninsula, lies along the Caspian
Sea coast. The lowland part of the Shirvan
steppe is located to the east of Goychay
River at the foothill of the southern mountainside
of Caucasian chain. The Lankaran zone takes
the southeastern part of Azerbaijan. As
to the landscape, it is divided into two
parts - offshore line forms up Lankaran
lowland and Talish Mountains rise in the
southwestern part. The border with Iran
passes through the highest mountain range.
The highest peak of the Talish inside Azerbaijan
is Kuzyurdu Mountain, which height is 2436
m.
Mud volcanoes
Mud volcanoes are a unique phenomenon in
the territory of Azerbaijan. The majority
of these volcanoes erupt a mixture of mud,
water and gas almost uninterruptedly. The
real sight is the eruption of the mud volcanoes
which is accompanied with the spreading
of the mudflow, throwing the tongues of
flame, ash and stones. Mud volcanoes might
also be continental and offshore. Nearly
400 among 800 mud volcanoes in our planet
are in Azerbaijan. There is no territory
in the world similar to Azerbaijan by number
of the volcanoes, their variety and activity.
That is why, Azerbaijan is considered the
Motherland of mud volcanoes. Some of volcanoes
are in the list of UNESCO sites as specially
kept monuments of nature. The largest mud
volcanoes in Caucasus and world is Taragay
- over 410 m located in the south of Gobustan.
There is also a unique volcano in the world
- Goturdag volcano, where constant eruption
has been taking place for many years.
Water resources
The Caspian Sea-Lake is a unique reservoir
of the planet, the remains of the ancient
ocean "Tesis" covering the whole
Caucasus in the old ages. It is called a
sea due to its territory area and number
of the hydrologic specifications. It washes
coasts of five states - the Russian Federation,
Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran and Azerbaijan.
More than 70 names of the Caspian Sea are
known: Khazar (name of the Turkic tribes),
Caspian, Khavilnsky, Baku, Gurgan, Darband
etc. The Caspian has features of both a
sea and a lake. Sea features are as follows:
huge area and water volume, strong storm
action, chemical hydrology similar to a
sea. Lake features: surrounded by land,
distance to the closest ocean is over 1000
km. In winter the sea is not calm, often
storms are observed here.
The level of the Sea over the whole history
of the Caspian has varied considerably.
It increased from- 29,0 m in 1978 to- 26,5
m in 1995 for 18 years. At present, it is
27 m below the level of the World Ocean.
The current Caspian is of great importance
for Azerbaijan. It softens climate, serves
as the important transport mean, is rich
with oil and fish, supports sanatoriums,
health resorts, that are built on the coast.
Let's pay attention to the physical map
of Azerbaijan. A rich river net of the Republic
covers its territory with a blue web. Almost
seven and a half thousand rivers exist,
small and non-deep as rule, they do not
exceed the length of five kilometers. However,
the main water artery of the country is
the Kur with the inflow on the right - Araz
crosses the whole Republic. Kur is also
called indomitable river. There are many
small lakes, wonderful of which is Goy-gol
("Blue lake") is high in the mountains.
The territory of the Republic is rich with
underwater, thermal and mineral springs.
Herbal features of "Sirab", "Istisu",
"Badamli" are popular far from
Azerbaijan.
|
 Climate Climate |
Occupying a considerably small territory,
Azerbaijan has unique natural-climate features.
Nine of 11 climatic zones of our planet are
in the territory of Azerbaijan: from subtropics
to Alpine mountains.
Climate conditions are multifarious. This
is provided by the allocation of the territory
at the turn of temperate zone and subtropics.
That is why the annual difference of the
temperatures in various regions of the republic
might exceed 60 degrees centigrade.
It is not a coincidence that Azerbaijan
is named "sunny country", because
the amount of sunshine reaches 2900 hours
a year. Sunny radiation has an impact on
the formation of the climate of the Republic:
from dry subtropics to temperature and cold
zone. If mountainous citizens may walk in
boots and sheepskin coats in spring, local
fashionable women actively demonstrate the
open clothes in the fresh air in the coastal
fields.
Often winds also have an impact on the
climate. The spped of the northern "khazri"
winds sometimes reaches forty meters a second,
which damages a lot of fields of the economy.
However, it brings desired coolness in summer.
Southern "gilavar" in winter promotes
to the clear weather, in summer - dry and
hot weather.
Precipitations are divided rather unevenly.
Less than 200 mm of precipitations are in
the southern coast of Absheron peninsula,
in the southeastern Shirvan and southeastern
Gobustan (foothills of Great Caucasus),
in Lankaran region - 1200 -1400 mm (sometimes
up to 1700 - 1800 mm). Most rainfall appears
in the cold season in Lankaran region, in
the remaining regions and foothills - from
April to September.
All four seasons of the year might be observed
in Azerbaijan simultaneously, such that,
the magnificent plants of the damp subtropics
neighbor with the zone of eternal snow and
ice of Shahdag and Murovdag while the forests
are filled with the spring aroma in Ismayilli,
Lachin, kalbajar. Contrast this with the
hot Mil, Mugan and Shirvan steppes and fog
with rain over the tea and citrus plantations
in the foothills of Talish and the gusty
nord - khazri winds in Absheron.
The Azerbaijan intend to sun themselves
in numerous Absheron beaches in summer months
- from May to September, have enough swimming
in the warm gentle Caspian waters.
Neither plentiful nor long snowfalls are
characterized for the local winters.

Treasures of the soil
Azerbaijan is a of oil and Azeri oil is
highly valued in the world market by its
characteristics. 47 thousand sq. km out
of the total area of the country (86.6 thousand
sq. km) area oil and territories. Specialists
say that underground fields in the territory
of the republic total to no less than three
billion tons of oil. Such potential attracts
attention of the leading oil companies of
the world. Azeri oilmen have been cooperating
with number of foreign companies in the
framework of the realized project since
1994.
Azerbaijan owns huge mineral-raw sources
of 340 nomenclatures. So, base of minerals
and raw materials on 28 kinds of the minerals
in 1991 was esteemed at 36.6 billion US
dollars.
 Fauna
and flora Fauna
and flora |
15 preserves and 20 reserves have been established
with the purpose of defense of planting and
animals.
The largest preserves of Azerbaijan are Zagatala
and Gizilgaj, which united the various reps
of the animals of the republic in their territories.
Ducks and sea gulls neighbor here with the
herons, cormorants, pelicans, and have "guests"
in summer, such as flamingo. The gulf near
the mouth of the Kur serves as a rich spawning
ground for 16 valuable fish species, and his
home to up to 200 species of birds. A lot
of Amphibians and creepers are characterized
for the coastal zone.
The main surviving inhabitant of Shirvan
preserve is the deer like Jeyran. You may
see the herds and lone animals, little jeyrans
with their mothers here. Sultan birds, bustard,
little bustard, marble teal, spoon-bill
are rare and disappearing species of the
birds listed in the Red Book and can be
see only on this depended territory.
In order to see the living monuments of
history, you should go to one of the must
wonderful places of Azerbaijan - Girkan
preserve. A relic grove of the lignum vitae
and chestnut-leaf oak, which impress with
their power and magnificence, is here. Local
citizens consider the lignum vitae as sacred.
As the people say, if you embrace a tree
before sunset and dream a wish, it will
definitely come true. Dappled deer, Talish
pheasant are also decoration of these places.
Goy-gol preserve is engaged in the defense
and study of typical landscapes and fauna
of Lesser Caucasus, re-acclimatization of
the noble deer, provision for the cleaning
of the water of one of the most beautiful
lakes of the world - Goygol as a source
of the drinking water.
31 species of trees among 107 existing
in the territory of Azerbaijan are in Ilisu
preserve. Mainly, these are oak, hornbeam,
and beech. Ash-tree, maple, nut-tree, willow,
as well as wild-growing fruit trees - apple-tree,
pear, sweet cherry. Dog rose, blackberry
etc. are among the bushes. Particularly
valuable species (relic and endemic) are
the following: bear filbert, Caucasian persimmon,
chestnut, Azeri dog rose etc. Animals are
represented by 35 species. Bear can be seen
quite often. Deer, Dagestan goat, boar,
wolf, fox, squirrel, badger, raccoon, hare,
hedgehog etc. are also widely spread.
Dagestan goats, Asia Minor moufflons, marals,
Caucasian charnoises and roe deer, in the
semi-deserts - jeyrans, foxes and jackals
can be seen in the foothill regions. Hens,
lynxes, porcupines, leopards and panthers
are widely spread here. In autumn months,
when the nuts and oak cones are ripened,
the "feast" of the boars and bears
start in the forests.
Besides the oak, beech and hornbeam are
also growing here and Kur banks are covered
with so-called Tugay forests. Rare species
of the trees grow in the foothills of the
Talish mountains: box tree, silk acacia,
lignum vitae, dzelkwa and yew. There is
expanse of sub-Alpine and Alpine meadows
high in the mountains. There are over 4000
species of plants in Azerbaijan, among of
which there are herbal greens and bushes.
|

