 Introduction Introduction |

Herodotus, the ancient Greek historian and traveller, once described Egypt as "the gift of the Nile", and since long before the birth of Christ, travellers have been drawn by images of pyramids, the Sphinx, ancient Luxor and the Nile river.
The Pharaohs, the Greeks, the Romans, the Arabs, the Turks, the French and the British have all ruled Egypt, and modern Egypt is an amalgam of these legacies and the influences of Islam and the 20th century.
Mud-brick villages stand beside Pharaonic ruins surrounded by buildings of steel, stone and glass. Bedouins live in goatskin tents and farmers till the earth with the simple tools of their ancestors. Townsfolk dress in long flowing robes, others in Levis and Reeboks, and city traffic competes with donkey-drawn carts and wandering goats. Nowhere are these contrasts played out so colourfully as in Cairo, a massive city thronged with people and ringing to the sound of car horns, ghetto-blasters and muezzins summoning the faithful to prayer. Egypt isn't all chaos and clatter, however. It's also a diver's dream dip, a quiet camel caravan through the desert or a long lazy punt down the Nile.
 GEOGRAPHY GEOGRAPHY |
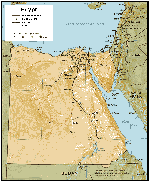
Click to enlarge (167ko)
Hacking a whopping square chunk out of Africa's north-east corner, Egypt stretches over more than a million square km. More than 90% of the land area is barren desert though, which has induced 99% of the population to squish into just 3% of the total land area, the fertile Nile Valley and Delta.
Egypt borders Libya in the west, Sudan in the south, the Mediterranean Sea in the north, and the Red Sea and Israel in the east. The eastern region, across the Suez Canal, is Sinai. This region slopes up to the high mountains of Mt Catherine (Gebel Katherina at 2642 meters is Egypt's highest point) and Mt Sinai. Along Egypt's Mediterranean coast there are countless white-sand beaches, some developed as tourist resorts but many still pristine and isolated. North of Cairo the Nile splits into a series of tributaries that flow into the Mediterranean.

Full country name: Arab Republic of Egypt (El-Gumhorriya Masr El-Arabiya)
Area: 1,002,000 sq km
Population: 62 359 623 (quarter of the total population of the Arab world).
Capital city: Cairo (largest city in Africa and the Middle East with 16 million people. Alexandria: 3 million, second Egypt's city)
People: Berbers, Bedouins and Nubians
Language: Arabic (however, English and French are widely spoken).
Religion: 90% Islam, 7% Christian
Government: Democracy
President: Mohammed Hosni Mubarak
Time Zones: 2 hours ahead of GTM
 CLIMAT CLIMAT |
Egypt's climate is hot and dry most of the year. During the winter months -December, January and February- average daily temperatures stay up around 20 degrees Celsius (68 degrees Fahrenheit) on the Mediterranean coast and a pleasant 26 degrees Celsius (80 degrees Fahrenheit) in Aswan. Maximum temperatures get to 31 degrees Celsius (88 degrees Fahrenheit) and 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit) respectively. Winter nights only get down to 8 degrees Celsius, a very Egyptian version of chilly. Alexandria receives the most rain with 19 cm each year, while Aswan is almost bone-dry with just 2 mm annually. Between March and April the khamsin blows in from the Western Desert at up to 150 km per hour. This nasty hot sandstorm blows variably, lasting 3-8 hours, but rarely more than once a week.
 MAJOR SECTORS MAJOR SECTORS |
Agricultural accounts for 36% of the total employment. Major crops include cotton, sugar cane, rice, corn, citrus wheat and a variety of vegetebles and fruits.
A wide range of industrial investments have emerged with the private sector now accounting for 60% of the industrial sector. Many businesses and plants have now obtained ISO accreditation.
Egypt has two main services sectors, the Suez Canal and Tourism. Egypt's tourism industry is now estimated at US$ 3.5 billion a year, while revenues from the Suez Canal are estimated at US$ 2 billion a year.
Petroleum and natural gas sector account for 10% of Egypt's GDP, with petroleum products accounting for 52% of Egypt's total exports. Natural gas accounts for 28% of the energy consumption in Egypt.
| Reclamation of the desert |
The government is preparing to turn huge swathes of desert into farmland. If it succeeds, the next generation of Egyptians could be living in 25%, rather than 5%, of their country's square kilometers. If the population goes on growing at its current rate of 2.1% a year, Egypt will reach 85 million by 2010.
The Al-Salam canal, completed in 1997, carries Nile water across the northern Sinai peninsula. The New Delta project will suck water straight from Lake Nasser behind the High Dam at Aswan, then sent it on a 500 km journey to link a string of desert oases into sort of parallel Nile valley. These schemes are expected to put more than 600,000 new hectares under the plough, providing a living for hundreds of thousands of people.
In the mid-1980s the government began to sell hudge chunks of desert land and to built condominiums on the beach. At present the Red Sea coast attracts only one-tenth of Egypt's tourists. Given current growth rates, the governemnt sees that share rising to about half the 10 million visitors expected each year by 2020. At least 90,000 hotel rooms must be built to accommodate them (which is 25% morethan the country's total capacity today).
Since 1991, the Egyptian banking sector has successfully completed its transformation from a highly regulated sector to a deregulated competitive industry. More people have started to use cheques, and several banks have seen an unprecedented increase in the demand for credit and debit cards. POS and ATM networks are being deployed throughout Egypt.
Marketing venues in Cairo include the annual March Cairo International Fair which is of a very broad scope and open to the public. However, specialized expos in various fields are held throughout th year either at Cairo's Conference Center or in several of Cairo's larger hotels.
 MODERN GOVERNMENT & POLITICAL PARTIES MODERN GOVERNMENT & POLITICAL PARTIES |
Egypt's strongly centralized government operates in principle as a political democracy with executive, legislative and judicial branches. In practice, and along with official democratic features such as a multiparty system, free elections, and a bicameral National Assembly, power resides heavily in the office of the president, supported by a large military bureaucracy, ministry heads appointed by the president, and a heavily nationalized industrial complex as part of a huge public sector-based economy.
President Mohammed Hosni Mubarak is serving his third six-year term (through 1999), and the head is the head of the ruling National Democratic Party (NDP). The NDP swept the last elections in November 1995 and continues to dominate the National assembly.
There are about ten legal opposition parties, the strongest of which are the Wafd Party (center-right), the Socialist labor Party, an the National Progressive Unionist Party (leftist). More influential in some senses is the outlawed Muslim Brotherhood party.
Egypt is divided into twenty-six governorates, each with a governor, local councils and ministerial representatives, and other appointed and elected officials. Greater Cairo is divided among three governorates, Giza (West of the Nile), Cairo (East of the Nile), and Qalyubiya (in the northern districts).
Egypt is a member of the Arab League.
|
 POLITICAL SYSTEM POLITICAL SYSTEM |
The permanent Constitution of the Arab Republic of Egypt, issued on september 11, 1970 and amended on May 22, 1980 is the most balanced constitution in Egypt's modern history.
The constitution includes 211 articles in seven chapters covering bases of the state, essential constituents of society and its economic components. It also defines freedoms, rights, public duties, principles and rule of law. It also defines the system of government, the executives, legislatives and judiciary authorities, local government and specialized national councils.
 System of Government System of Government |
According to the Constitution, the People's Assembly undertakes the legislative authority, approves the state's overall policy, the general socio-economic developments plan, the state general budget and controls the work of the executive authority.
| Shura (consultative) Council |
The Shura Council was established under a constitutional amendment issued on June 22, 1980 for the first time since July, 1952. The council was created in response to an inclination to expand the scope of democracy and partcipation by wider sectors of sages, intellectuals and seniors experts in formulating the nation's present and future and taking part in political decision-making.
The Shura Council is concerned with the study and presentation of proposals on issues submitted thereto as well as matters referred to by the President of the Republic, relating to overall state policy or sovereignty rights.
The Shura Council is composed of 264 members of whom two thirds are elected by direct public secret ballot provided that at least one half of the members are workers and peasants representatives. The Head of the state appoints the remaining third so that the council truly represents all political powers and specialised and popular trends.
 Executive Authority Executive Authority |
The Head of the States undertakes the executive authority, and in conjunction with the Cabinet, lays down and supervises the implementation of public policy. He is also the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces and presides over the Police Supreme Council and the National Defense Council.
It is the supreme administrative and executive body of the State, represented by the Cabinet which administers the affairs of the Government as defined by the constitution follows:
Direct, coordinate and monitor the performance of ministries, public agencies, organizations and authorities.
Prepare bills, draft laws and decisions.
Draft general state budget and the state's draft overall plan.
Conclude and grant loans.
| Cabinet members (updated July 2000) |
Prime Minister Mr. Atef Mohamed EBEID
Min. of Agriculture & Land Reclamation Mr. Youssef Amin WALLY
Min. of Awqaf (Religious Affairs) Mr. Mahmoud Hamdy ZAQZOUQ
Min. of Communication & Information Technology Mr. Ahmed Mahmoud NAZIF
Min. of Construction, Housing, & New Urban Communities Mr. Mohamed Ibrahim SOLIMAN
Min. of Culture Mr. Farouq HOSNI
Min. of Defense & Military Production Mr. Mohamed Hussein TANTAWI
Min. of Economy & Foreign Trade Mr. Youssef BOUTROS-GHALI
Min. of Education Mr. Hussein BAHA Al-DIN
Min. of Electricity & Energy Mr. Ali Fahmy AL-SAEDY
Min. of Finance Mr. Muhammad Medhat HASSANEIN
Min. of Foreign Affairs Mr. Amr Mahmoud MOUSSA
Min. of Health & Population Mr. Ismail Awadallah SALLAM
Min. of Higher Education & Scientific Research Mr. Munfeed SHEHAB
Min. of Industry & Technology Development Mr. Mustafa Mohamed EL-RIFA'I
Min. of Information Mr. Mohamed Safwat EL-SHERIF
Min. of Insurance & Social Affairs Mme. Amina EL-GUINDI
Min. of Interior Mr. Habib EL-ADLI
Min. of Justice Mr. Farouq Seif EL-NASR
Min. of Manpower& Immigration Mr. Ahmed EL-AMAWY
Min. of Petroleum Mr. Sameh FAHMY
Min. of Planning Mr. Ahmed Mahrus EL-DARSH
Min. of Public Business Sector Mr. Mokhtar KHATTAB
Min. of Water Resources & Irrigation Mr. Mahmoud Abd El-Halim ABU ZEID
Min. of Supply & Internal Trade Mr. Hassan Ali KHEDR
Min. of Tourism Mr. Mamdouh EL-BELTAGUI
Min. of Transport Mr. Ibrahim EL-DEMERI
Min. of Youth Mr. Ali El-Din Hillal DESSOUKI
Min. of State for Administrative Development Mr. Mohamed Zaki ABU AMER
Min. of State for Environment Affairs Mme. Nadia Riad Makram EBEID
Min. of State for International Co-operation Mr. Ahmed Mahrus EL-DARSH
Min. of State for Local Development Mr. Mustafa Abdel QADER
Min. of State for Military Production Mr. Sayrd MESH'AL
Min. of State for People's Assembly & Consultative Council Affairs Mr. Kamal El-Shazly,
Min. of State for Scientific Research Mr. Mufed SHEHAB
The Judiciary Authority is an independent authority assumed by courts of justice of different types and categories. Court issur their verdicts in accordance with the law. Judges are independent and are governed exclusively by the authority of the law. No authority shall intervene in lawsuits or affairs of justice. In addition, judges are immune from discharge.
The role of the judiciary in formalizing political parties is an expression of its growing activity in promoting democracy an party plurality.
The Supreme Constitutional Court on one hand and the State Council's Board of Commissioners on the other play a significant role in establishing the principles of public freedoms.
The Supreme Constitutional Court exclusively exercices judiciary control to ensure that laws and regulations comply with the Constitution and undertakes the task of interpreting legislative provisions.
The Arab Repuplic of Egypt is divided into administrative units each considered as a corporate body, including gouvernorates, cities and villages. Local people's councils are formed, by direct election on graduated levels at administrative units, providing that at least half of their members are workers and peasants. Chairmen and vice-chairmen of such councils are elected from among their members.
Local government units also shall approve the conclusion of loans for productive projects, demarcating industrial estates, setting up services, committees and land reclamation projects within the juridiction of the local unit.
 CALENDAR & PUBLIC HOLIDAYS CALENDAR & PUBLIC HOLIDAYS |
The Islamic (or Hjira) calendar, which is a Lunar Calendar, is a full 11 days shorter than the Gregorian (western) calendar, so public holidays and festivals fall 11 days earlier each year. Moslem holidays do not necessarily fall on the same day as other Arab or Moslem countries as it depends on the country's longitude which affects the sighting of the moon.
Ras As-Sana is the celebration of the new Islamic year, and Mouled An-Nabi celebrates the prophet Mohammed's birthday around July/August. These celebrations include parades in the city streets with lights, feasts, drummers and special sweets. Ramadan is celebrated during the ninth month of the Islamic calender (presently around January/February/March) and this is important in the Islamic year. During this month the Qur'an was revealed to Mohammed, and out of deference the faithful take neither food nor water until after sunset each day. At the end of Ramadan -Eid Al-Fitr- the fasting breaks with much celebration and gaiety. Eid Al-Adhah is the time of the pilgrimage to Mecca, and each Muslim is expected to make the pilgrimage at least once in a lifetime. Streets are decorated with coloured lights and children play in their best clothes. The ritual of Mahmal is performed in each village as passing pilgrims are given carpets and shrouds to take on their journey. This all happens around April/May.
January 1: New Year's Day
January 7: Coptic Christian Christmas
April 25: Sinai Liberation Day
May 1: Labor Day
July 23: National Day
October 6: Armed Forces Day |
Ramadan Bairam (End of Ramadan Fasting Month)
Sham El-Nessim (Spring Day)
Eid Al-Adhah (Pilgrimage Feast)
Islamic New Year
Mouled En-Nabi (Prophet's Birthday) |
|

